AD9371
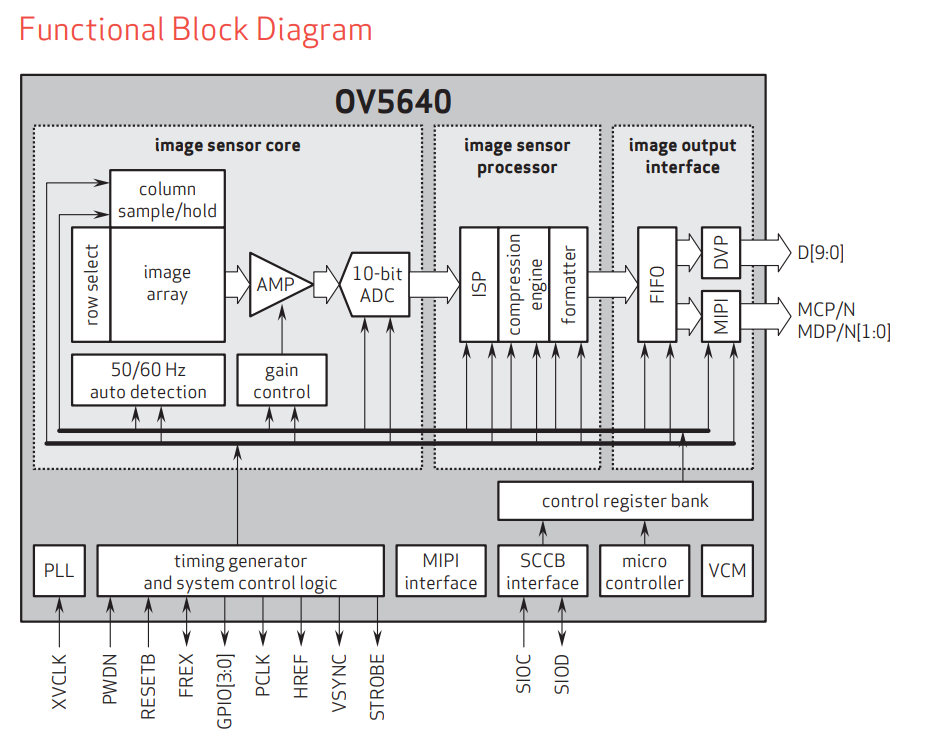
What is AD9371 ? The AD9371 is a highly integrated, wideband RF transceiver offering dual channel transmitters and receivers, integrated synthesizers, and digital signal processing functions. The IC delivers a versatile combination of high performance and low power consumption required by 3G/4G micro and macro BTS equipment in both FDD and TDD applications. The AD9371 operates from 300 MHz to 6000 MHz, covering most of the licensed and unlicensed cellular bands. The IC supports receiver bandwidths up to 100 MHz. It also supports observation receiver and transmit synthesis bandwidths up…
Read More