The Use of SignalTap Logic Analyzer, Analyze the Captured Signals – FPGA Beginner Study Board PRA006, PRA010 Experiment 2
Experiment 2 SignalTap
2.1 Experiment Objective
- Continue to practice using of the development board hardware;
- Practice the use of SignalTap Logic Analyzer in Quartus;
- Learn to analyze the captured signals.
2.2 Experiment Implement
Capture and analyze the switching signals on the development board through the use of SignalTap.
2.3 Experiment
2.3.1 Introduction to the Switches and SignalTap
- Introduction to the switches
The on-board switch is 8 DIP switches, as shown in Figure 2.1. The switch is used to switch the circuit by turning the switch handle using the binary coding principle of 0/1.
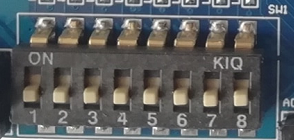
Figure 2.1 DIP switches physical picture
- Introduction to the SignalTap
SignalTap uses embedded logic analyzers to send signal data to SignalTap for real-time analysis of internal node signals and I/O pins when the system is operating normally.
2.3.2 Hardware Design
The schematics of the switch is shown in Figure 2.2 (In the red rectangular). One port of the 8 switches is connected to BANK_VADJ at the same time, which is in high level. The other port is respectively connected with an LED, and is connected to the control terminal SW_LED end of the LEDs. When the DIP switch is strobed, the high level turns on the FET, the LED is on, and a high level signal is input to the FPGA at the same time. 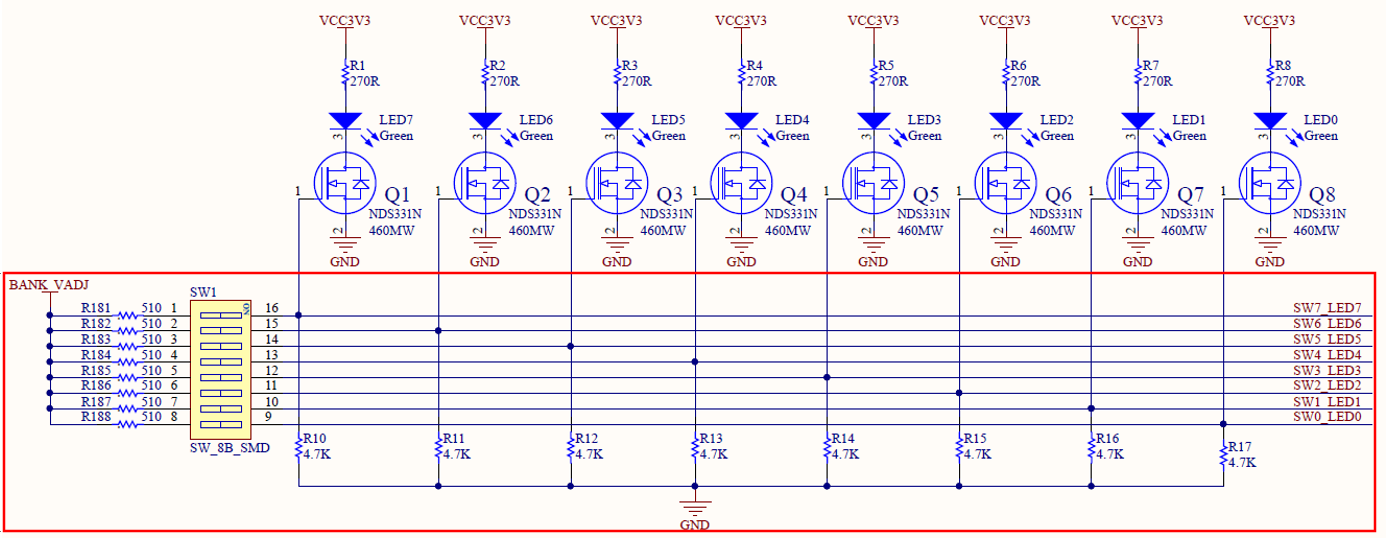
Figure 2.2 Schematics of the switches
2.3.3 Program Design
The first step: the establishment of the main program framework (interface design)
| module SW_LED(
input clk, input [7:0] sw, output reg [7:0] led ); endmodule |
The experimental input signals have a system clock clk with frequency of 50 MHz, an high effective 8-bit switch sw, and an output 8-bit led.
2.4 Use and Verification of SignalTap Logic Analyzer
The first step: pin assignment
Pin assignments are shown in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 Pin mapping
| Signal Name | Network Label | FPGA Pin | Port Description |
| clk | C10_50MCLK | 91 | Input clock |
| rst | KEY3 | 10 | Reset |
| SW[7] | SW7_LED7 | 77 | SW 7 |
| SW[6] | SW6_LED6 | 76 | SW 6 |
| SW[5] | SW5_LED5 | 75 | SW 5 |
| SW[4] | SW4_LED4 | 74 | SW 4 |
| SW[3] | SW3_LED3 | 87 | SW 3 |
| SW[2] | SW2_LED2 | 86 | SW 2 |
| SW[1] | SW1_LED1 | 83 | SW 1 |
| SW[0] | SW0_LED0 | 80 | SW 0 |
The second step: SignalTap II setupa dn basic settings
Menu Tools > SignalTap II logic Analyzer,
- In Figure 2.3, set the data under Signal Configuration
- Set the JTAG configuration and click on Setup to set the downloader.
- Set the device type by clicking Scan Chain
- Set up SOF Manager: set as *.SOF that is just compiled and generated before
- Clock and storage depth settings are shown in Figure 2.4.
Click the position shown in Figure 2.4 to add the clock. As shown in Figure 2.5, in the Clock Settings dialog box: Filter select SignalTap: pre-synthesis -> List, select the desired clock signal, select c0 in PLL1: PLL1_INST, move to the box on the right.
Other settings can be set as shown in Figure 2.2. (for advanced use of SignalTap II, please read the Intel reference files)
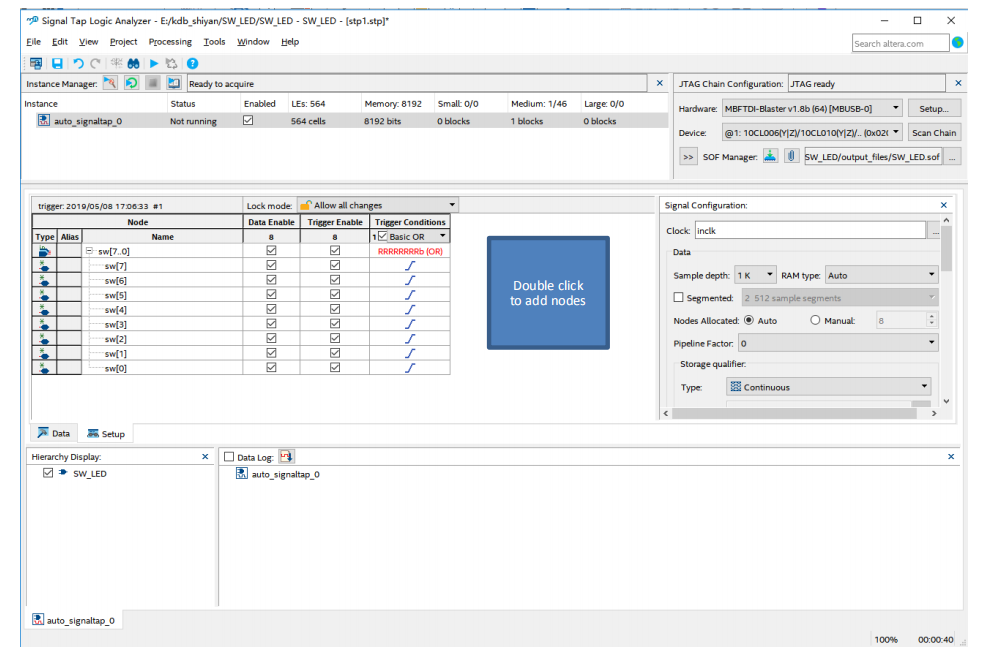
Figure 2.3 SignalTap setting
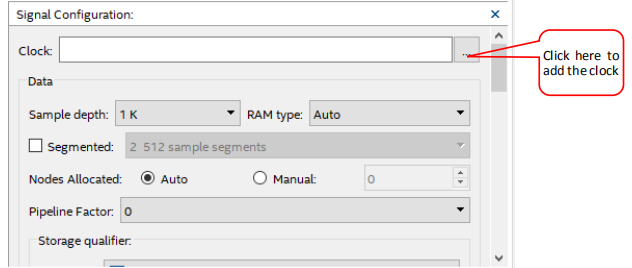
Figure 2.4 Clock signal and the sample depth
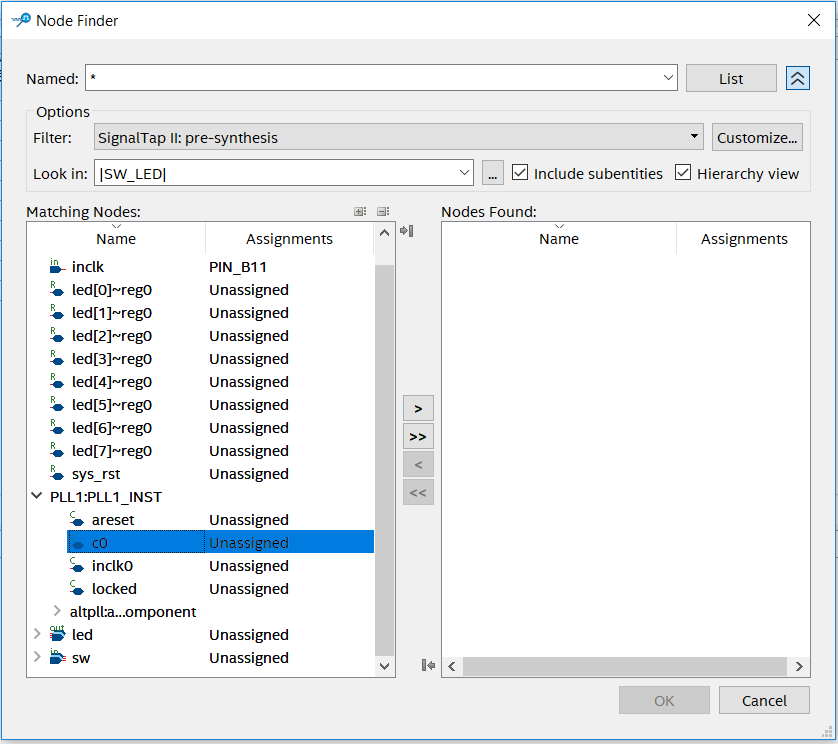
Figure 2.5 Clock signal selection dialogue
The third step: add observation signals
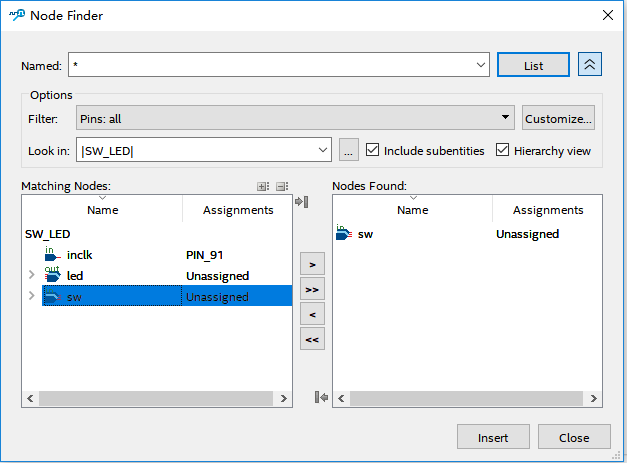
Figure 2.6 Adding interface for the observation signals
As shown in Figure 2.3, double-click the blank space to add the observation signal. Adding interface is shown in Figure 2.6. Select the signal to observe on the left side, add it to the right side, click Insert. Save it and recompile.
The fourth step: setting of observation signals
For the signal to be observed, whether it is a rising edge trigger, a falling edge trigger, or not care, etc., needs to be manually adjusted, as shown in Figure 2.7.
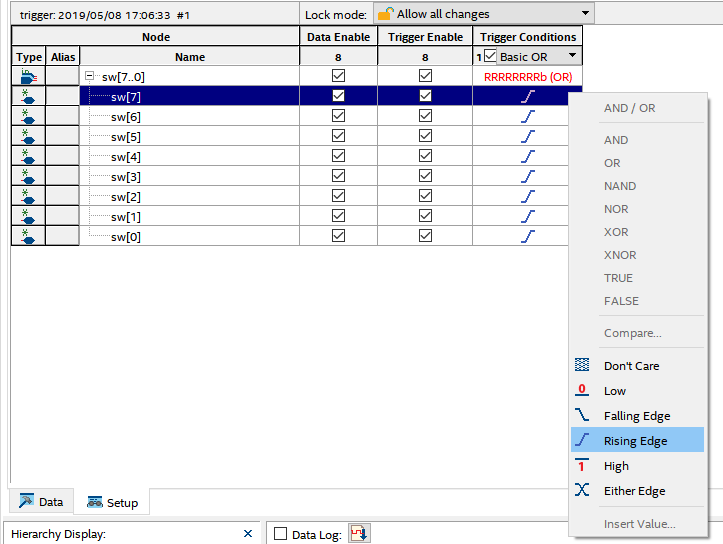
Figure 2.7 Trigger signal setting
The fifth step: observe the result
As shown in Figure 2.8, click Run Analysis to observe the output of SignalTap.
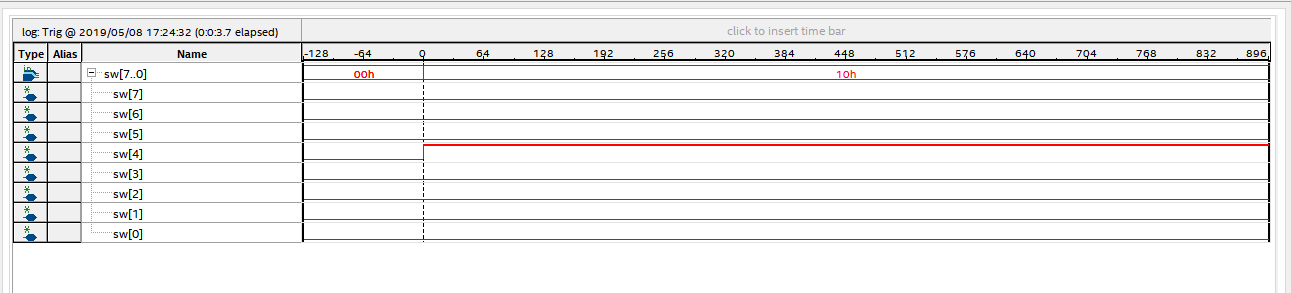
Figure 2.8 Experiment result
After the switch sw[4] is turned on, its signal is high, and the corresponding LED will be lit.
Modify the Trigger condition, test the output results under different Trigger conditions, analyze and summarize the experiment results.