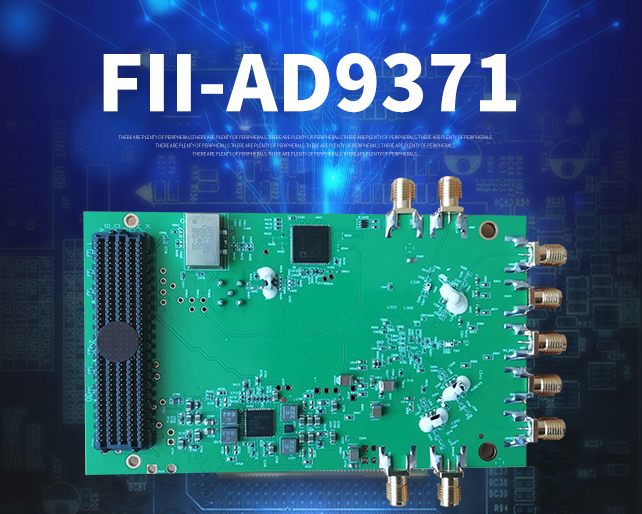
AD9361
The AD9361 is a high performance, highly integrated radio frequency (RF) Agile Transceiver™ designed for use in 3G and 4G base station applications. It is developed and manufactured by Analog Devices company. Its programmability and wideband capability make it ideal for a broad range of transceiver applications. The device combines a RF front end with a flexible mixed-signal baseband section and integrated frequency synthesizers, simplifying design-in by providing a configurable digital interface to a processor. The AD9361 receiver LO operates from 70 MHz to 6.0 GHz and the transmitter…
Read More