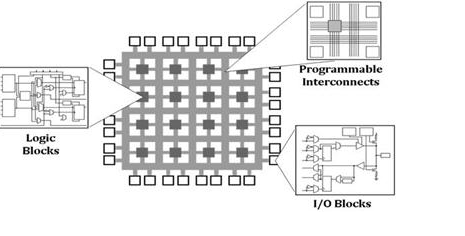
FPGA
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are semiconductor devices that are based around a matrix of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) connected via programmable interconnects. FPGAs can be reprogrammed to desired application or functionality requirements after manufacturing. A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturing – hence the term “field-programmable”. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this…
Read More